What is CBD and how does it work in animals?
Are you a vet who is considering prescribing CBD for a pet but don’t quite understand how the treatment works? Are you a pet owner who is interested in exploring the CBD therapy for your pet? Let’s dive in and explore what CBD is, and discuss how the compound operates on a biological level.
What is CBD?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid found in the cannabis plant species. It was discovered in the 1940s and has been researched for a wide range of medicinal uses in humans.
In recent years, the amount of studies conducted regarding the use of CBD for household pets has grown exponentially.
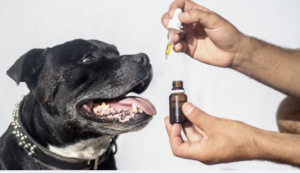
CBD can be isolated naturally from the Cannabis Sativa plant and can also be made synthetically. Currently, only CBD oil that has been obtained from a natural source is legal to be supplied in Australia. We supply CBD in an oil formulation, and can add flavouring if desired.
CBD acts as an additional tool for use in animals alongside more traditional veterinary treatments. It can be used to enhance treatment outcomes for a wide variety of conditions in animals such as epilepsy, osteoarthritis, chronic pain, anxiety, and appetite loss.
Difference between CBD and other cannabinoids
CBD is one of many cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. Another well-known compound in the cannabis plant is delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Whilst coming from the same plant, CBD and THC are distinctly different compounds.
THC is the most active constituent of cannabis and it has psychoactive properties. It creates a mind-altering “high” when a person smokes it or ingests it orally.
CBD, in contrast, is not psychoactive. It does not change a being’s state of mind when they take it. CBD has been shown to have medicinal properties and it can elicit significant changes in the body.
How does CBD work in the body?
CBD works through its relationship with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is universal to humans and all animal species (except insects).
The ECS is a complex system which is interdependent and interwoven with pretty much every other system in the body. The ECS is said to maintain homeostasis in the body. Cannabinoid research, Professor Vincenzo Di Marzo, summarises the functions of the ECS in 5 words, ‘relax, eat, sleep, forget, protect’.
The ECS has dynamic relationships with the immune, digestive, cardiovascular, and nervous systems, making the ECS consequential in everything from regulating blood pressure, to appetite control, and so much more.

What is the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?
The endocannabinoid system functions through the stimulation of cannabinoid receptors. This stimulation can be induced by either endocannabinoids (produced naturally in the body) or by phytocannabinoids such as CBD (produced in the cannabis plant).
The two main cannabinoid receptors are G protein-coupled receptors, referred to as CB1 and CB2. Both receptor types are found dispersed throughout the body with different areas of density.
CB1 receptors are abundant in the brain and nervous system and are primarily famous for their interaction with THC – facilitating the intoxicating effects of cannabis. Beyond the euphoric effects, CB1 receptors also contribute to maintaining biological balance via processes in the nervous and endocrine systems. In modulating hormonal release, influencing serotonin, dopamine and regulatory pathways they have both a direct and indirect role in mood, sleep, stress and pain.
CB1 receptors are also found in the cardiovascular and digestive system. In the heart, CB1 receptors moderate dilation and contraction of vessels thereby maintaining blood pressure. In the gastrointestinal tract they have influence over appetite hormones, motility and secretions.
CB2 receptors do not modulate the euphoric or intoxicating effects of cannabis or endocannabinoids but have a strong presence in the immune and reproductive systems. They are key mediators in the regulation of inflammation, pain and digestion, while in the skeletal system they are believed to play a role in maintaining bone density.
How does CBD interact with the Endocannabinoid System?
Numerous other receptors play a part in this orchestra. For example, CBD interacts with other receptors such as TRPV1 and PPAR-gamma, as well as indirectly influencing ECS processes.
It is the activation of these receptors that are thought to account for CBD’s positive benefits in neuroprotection, pain, and inflammatory conditions.
The bliss-inducing endocannabinoid molecule, anandamide, has been shown to interact with serotonin receptors resulting in improved mood and pain relief. This molecule is believe to be responsible for the ‘runner’s high’.
Different animals express varying levels of these receptors, making them more or less susceptible to the effects of endocannabinoids and medical cannabis treatments.
In particular, dogs and cats seem to have slightly different expressions of ECS components, making it incredibly important that medicinal cannabis prescriptions are administered by a trained veterinarian for the safety of the animals.
Prescribing CBD for animals
If you are a pet parent considering CBD for your pet please talk to your vet.
If you are a vet who has a pet patient who may benefit from CBD, follow these simple steps to start prescribing CBD today:
- REGISTER WITH US: Complete this short form to gain access to our online Vet Portal for research material, prescribing information, case studies, training videos, and more.
- WRITE A SCRIPT. Fill out a prescription order form online, or send it by email, when you have an animal patient who may benefit from CBD.
- DIRECT DELIVERY: The prescribed CBD oil will be posted directly to your clinic or to the pet owner, usually within a couple of days.
If you would like some more information about prescribing CBD to animals, please feel free to get in touch at [email protected]
Edited by Emma Delaney, MPharm